
Patients with advanced ovarian cancer need more effective and targeted drugs.
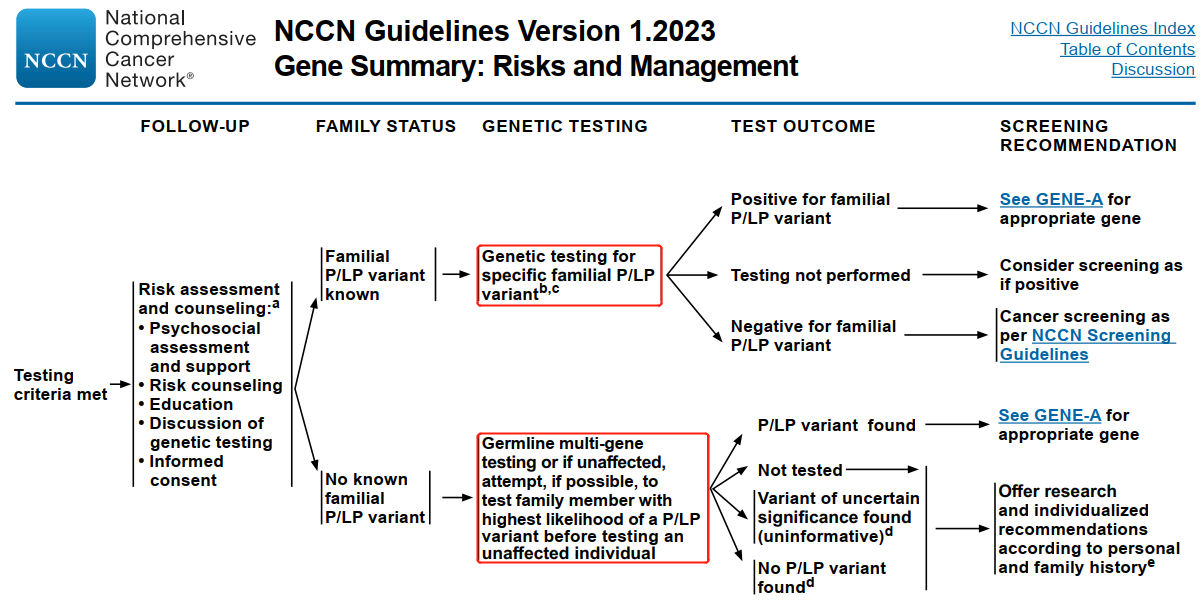
NCCN guideline recommendation: patients carrying BRCA1/2 gene mutations should be managed in according to the risk management measures for hereditary breast/ovarian cancer syndrome (HBOC).
Studies have found that 23% of ovarian cancers are associated with hereditary gene mutations, and 65-85% of hereditary ovarian cancers are caused by BRCA1/2 germline mutations. For the early diagnosis of ovarian cancer, relevant guidelines recommend gene detections for ovarian cancer patients and their relatives.
| Types of ovarian cancer patients requiringgene detection | Recommended guidelines |
| Ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and peritoneal cancer | SGO (Society of Gynecologic Oncology) |
| Invasive ovarian cancer | NCCN (National Comprehensive Cancer Network) |
| Epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer | ASCO (American Society of Clinical Oncology) |
| Non mucinous ovarian cancer and fallopian tube cancer | SIGN (Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network) |
| High-grade serous ovarian cancer and fallopian tube cancer | ACOG (American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists) |
Ovarian cancer patients carrying BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations are treated differently from non-carriers, and the mutation is associated with prolonged survival with chemotherapy. Ovarian cancer patients carrying BRCA mutations have more drug options for chemotherapy due to their sensitivity to chemotherapy. Gene detection has the following clinical significance:
Assess disease risk
It can identify women at a high genetic risk of ovarian cancer and help these groups and their families formulate preventive strategies in advance;
Currently, various international guidelines recommend a BRCA1/2 or multi-gene detection for all ovarian cancer patients.
Formulate treatment regimensIt can identify patients who are sensitive to platinum-based chemotherapy or who are candidates for targeted therapy (e.g. PARP inhibitors).
| Standard version BRCA1/2 | Professional version 17 genes |
| Gene sequencing technology is used to detect single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and small insertions/deletions (InDel) in the two coding regions of BRCA1/2 genes (totally 16,000 bases); Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) technology is used to detect large fragment rearrangement (LGRS) of BRCA1/2 genes. | BRCA1; BRCA2; PALB2; CDH1; CHEK2; ATM; PTEN; STK11; TP53; BAHD1; BFIP1; RAD51C; RAD51D; MLH1; MSH2; MSH6; PMS2 |

- All patients with ovarian cancer;
- Healthy family members of ovarian cancer patients who are mutation-positive by BRCA1/2 or multi-gene detection.


